Parenting style can be a major factor in what kind of person your child can become.
In this paper, the authors discuss how the different dynamics of parent-child interactions can predict the child’s social, emotional, and cognitive functioning. To make these predictions, the authors were concerned with these four features of the parent-child relationship:
- Parental control (parent’s consistency in enforcing rules, parent’s structuring of the child’s activities, and parent’s persistence in gaining child compliance)
- Maturity demands (parent’s expectations for the child to perform at their potential, parent’s demands for child to be self-reliant and have self-control)
- Clarity of communication (extent of parent’s interest in child’s opinions and feelings, parent’s use of reasoning to gain child compliance)
- Nurturance (parent’s expressions of warmth and approval, parent’s protection of child’s physical and emotional well-being)
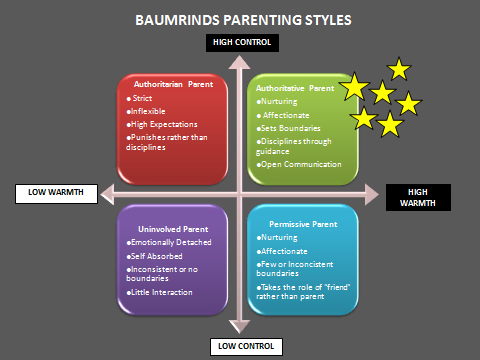
These four features were used to categorize parenting into four different parenting styles: authoritarian, authoritative, permissive indulgent, and passive.
AUTHORITATIVE
- Authoritative parenting is responsive and demanding in that parents communicate high expectations, provide clear standards for behaviour, monitor child behaviour, and discipline based on reasoning and explanation rather than power assertion or withdrawal of love.
- Elementary-aged children of authoritative parents display adaptive levels of self-reliance and self-esteem, and socially responsible, independent, and achievement-oriented behaviour;
- Adolescents with authoritative parents fared best with respect to a range of social, emotional, and academic competencies;
- Children with authoritative parents demonstrate competent social interaction skills, self-reliant and independent problem solving, emotional wellbeing and overall psychological adjustment, and few maladaptive internalizing and externalizing behaviours. These children enjoy academic success, demonstrate socially responsible and prosocial forms of classroom behaviour, and competent relationships with their peers. They also report strong intrinsic interest in learning, positive beliefs about ability and control, and mastery goal orientations toward learning.
The authoritative parenting style is the healthiest of styles. The children of authoritative parents have a healthy and secure bond with their parents. These parents have high expectations for their child, provide clear standards for behaviour, and they discipline based on reasoning and explanation rather than power assertion (aggression, yelling, hitting) and love withdrawal. Parents empower their children’s ability to make decisions, creating cooperative, confident, and self-motivated children. Children reared by authoritative parents are self-reliant, have good self-esteem, are independent and responsible, and are achievement-oriented. These children are predictably successful academically, they are typically the most altruistic, and have successful social relationships with peers._
________________________________________________________________________________
AUTHORITARIAN
- Authoritarian parenting is similar to authoritative parenting in terms of being demanding; however, parents are described as less responsive in that they are more likely to use power assertive disciplinary techniques and rely on love withdrawal to gain child obedience.
- Children with authoritarian parents display relatively less independent behaviour and lower levels of self-reliance and self-esteem; and
- Students with authoritarian parents reported relatively lower levels of psychological well-being;
The authoritarian parenting style is similar to the authoritative parenting style in that the parents are typically clear that they have high expectations for their children. However, instead of disciplining based on reasoning and discussion of the child’s misbehaviour, these parents are more likely to use power assertion (yelling, spanking, “because I said so” explanation, etc.) and love withdrawal. These techniques gain child compliance based on children feeling fear rather than respect and understanding. These children display less independence, low self-esteem, and low self-reliance. Children of authoritarian parents report lower levels of psychological well-being, and are typically an average to good student. These children may be labelled as a follower, and can have anxious tendencies while also being very well-behaved.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
PERMISSIVE INDULGENT
- Permissive indulgent parents display relatively high levels of responsiveness but low levels of control. Specifically, this style is typified by low levels of control and maturity demands, but high levels of solicitation and demonstrations of warmth.
- Children with permissive parents display less positive behaviour and self-reliance but high levels of self-esteem.
- Those with indulgent parents were characterized as enjoying high levels of psychological and emotional wellbeing but lower levels of achievement coupled with higher levels of misconduct
The permissive indulgent parenting style involves highly responsive and affectionate parents who provide little control and demonstrate few expectations from their children. Children raised in a permissive indulgent household generally have a high self-esteem but are less self-reliant and less empathetic. Typically, they are a poor or average student. Permissive parents are anxious to please (usually ends sentences with “okay?”) and so are easily manipulated by family and friends.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
PASSIVE / PERMISSIVE UNINVOLVED
- In contrast, passive [permissive uninvolved] parenting is described as being relatively low on both warmth and control. At its extreme, this style is considered to be rejecting or neglectful of children.
- Students with un-involved/neglectful parents were characterized as demonstrating the lowest levels of competence in all areas. Over the course of the high school years, the academic functioning of adolescents with neglectful parents declined and levels of delinquency and internalizing symptoms such as depression increased significantly, especially in comparison to that of students with authoritative parents.
Children raised in a passive/permissive uninvolved household typically perform poorly in school. Parents provide neither warmth nor control in the household, and so their children are quick to get into trouble at school. The parents are emotionally indifferent and inconsistent. Their children tend to be clingy and needy.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Parenting is the most difficult of all jobs. There is no perfect prescription because every child and every parent is different. However, from this and other research done on Baumrinds parenting styles, we know that a high warmth, high control type parenting results in the most well-adjusted children long term. Therefore, give yourself permission to be an Authoritative parent. Be nurturing and affectionate with open communication while at the same time setting clear boundaries and providing discipline through guidance. At Simone Friedman SLS, we provide workshops on how to do this. We coach parents and provide strategies that they can utilize to feel confident in the authoritative role.
Wentzel, K., & Russell, S. (2009, December 23). Parenting Styles. Retrieved March 29, 2016, from http://www.education.com/reference/article/parenting-styles1/